This documentation was created using Microsoft Word 365 for macOS.
Microsoft Word includes options for adding accessibility information to documents to support access by individuals with disabilities. This information also ensures that Microsoft Word files maintain a level of accessibility when converted into other formats (e.g., tagged PDF). Creating accessible Microsoft Word documents can be accomplished by incorporating the following practices into your authoring process.
Headings
Headings can provide an organizational and navigational framework for a document's content, communicating both the informational hierarchy and relationship between different sections. Headings also provide a simple mechanism for an individual using assistive technologies to "jump" from one heading to the next when navigating the document.
For more information about headings in general, see our article Use Headings and Lists in Support of Accessibility.
How to use Headings in Word:
- From the Home tab, choose the Styles pane. This will open the list of heading and other styles for use in the document.
- Place focus on the appropriate content and choose the relevant heading style.
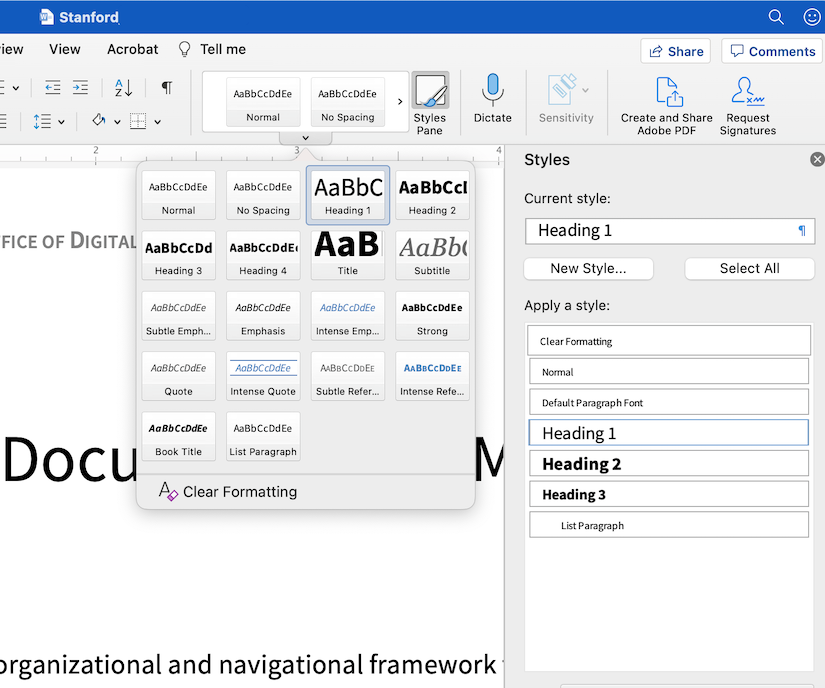
Headings can be marked with the following keyboard commands:
| Heading Function | macOS Command | Windows Command |
|---|---|---|
| Apply Heading 1 | Command + Option + 1 | Ctrl + Alt + 1 |
| Apply Heading 2 | Command + Option + 2 | Ctrl + Alt + 2 |
| Apply Heading 3 | Command + Option + 3 | Ctrl + Alt + 3 |
Technical guidelines
- Headings should follow a logical structure that identifies content based on the organizational content and hierarchy of information in the document.
- Avoid skipping heading levels - Modify Style of the heading if you prefer a specific font or appearance.
Formatting guidelines
- Headings should be short and succinct.
- The default Heading 1 and Heading 3 styles lack sufficient color contrast. Select a darker font color for these heading styles such as black or dark blue.
- To change the appearance of a heading, read Modify Styles in Microsoft Word for more information or follow the directions below:
- Highlight the heading.
- Use the font and formatting tools to change the appearance.
- Right-click the heading style.
- Select Update Heading to Match Selection. This option will automatically update all of the heading styles in the document to the desired format.
Lists
Lists provide a structured order to a group of connected or sequential content. A numbered or bulleted list may present the same information more effectively than simple data tables with fewer steps.
- Highlight the grouped list of items.
- In the Home tab, select the appropriate list style (i.e, numbered list or bulleted list).
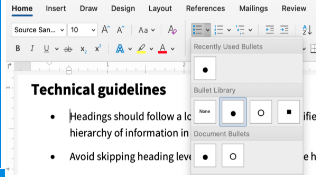
Formatting guidelines
- Remove any lists manually created, such as those using dashes or asterisk characters. Manual lists are not "true" lists.
- Avoid using indentation to provide a visual list in lieu of the list style button.
- Ordered or numbered lists are used to present a group of items (words, phrases, sentences) that follow a sequence.
- Unordered or bulleted lists are used for a group of items without a sequence.
- Lists should contain at least two or more list items, unless being used to create an outline.
- Nested lists are acceptable, such as a numbered list that contains a nested bulleted list.
Images
Images that support the content require a text description (also called "alt text") that communicates the purpose and/or content of the image. For more information about choosing appropriate alt text, see Create Accessible Images with Alt Text.
Adding Alt Text in Word
- Select and right-click the image.
- Select Edit Alt Text.
- Provide a brief and concise description and “X” or close the window.
Marking a decorative image
- Select the image.
- Right-click the image.
- Select Edit Alt Text.
- Select Mark as decorative.
Other recommendations
- "Behind Text" or "In Front of Text" image positioning settings are not recommended due to how this format setting can obscure text and make the content difficult or impossible to read.
- For older versions of Microsoft Word, leave the Title field blank, and only use the Description field for alt text.
Hyperlinks
Documents containing hyperlinks to websites or other online resources can be improved by including hyperlink text that is understood by the reader. For instance, using the full URL as the hyperlink text may not make sense to the reader, particularly if it is long. For more information about choosing good Hyperlink text, see Creating Accessible Links.
- Place the cursor anywhere on the desired hyperlink.
- Right-click the hyperlink. Select Hyperlink, then Edit Hyperlink.
- Under Text to Display, write the descriptive text for the hyperlink, keeping the text name short and descriptive.
- Select OK.
Tables
Tables in Microsoft Word should be used for data and not layout purposes. An accessible table includes:
- At least one header (row and/or column).
- An Alt Text description summarizing the table.
Apply at least one header
- Select the table to reveal Table Design. (Note: this tab will only appear if the table is selected.)
- In the far left-hand section, determine the required header type:
- Header row: check the box Header Row.
- Column header: check the box First Column.
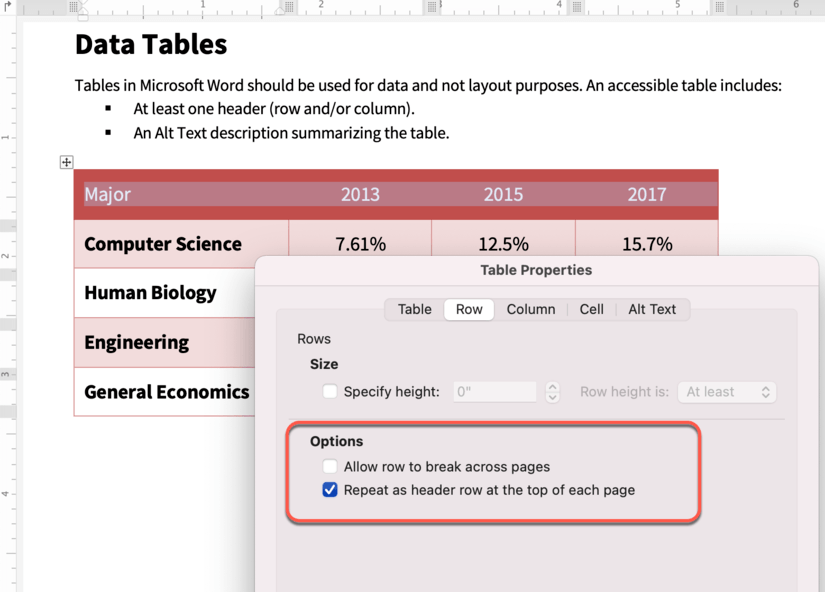
- Highlight the header row of your table. Right-click the table and Select Table Properties.
- In the Row tab, check the box Repeat as header row at the top of each page.
- In the Alt Text tab, write a short, one-sentence description of what the table information presents.
- Select OK.
Color
Color can be an effective method to communicate ideas and draw attention to information. Ensuring there is sufficient contrast as well as using color in combination with other formatting can support a diverse campus community, including individuals with visual disabilities.
For guidelines on using color, see Color Use and Accessibility.
Export to other formats
Including accessible authoring practices into Microsoft Word documents allows for versions exported as other formats to retain most, if not all, accessibility features. Do not use the "Print to PDF" function to create a PDF document. This will create a PDF document that lacks PDF tags with no heading information, no alternative text, and no logical document structure. These types of PDF documents will create barriers when accessing the document with assistive technologies.
Create a PDF from Microsoft Word with the Acrobat plug-in
It is much easier to create an accessible PDF document from an accessible MS Word document rather than trying to fix any accessibility issues afterward. If starting with a PDF, it is generally recommended to convert the file back to an MS Word version and then apply the appropriate accessibility techniques.
- Select the Acrobat tab in the MS Word ribbon.
- Select Create PDF.
- If using a Mac with Acrobat Adobe installed, select Best for electronic distribution and accessibility (uses Microsoft online service).
- Select Export.
Create a PDF from Microsoft Word without the Acrobat plug-in
If you do not have the Adobe Acrobat plug-in installed for Microsoft Word, you can still create an accessible, tagged PDF document. Creating an accessible PDF document from MS Word is much easier than trying to remediate the PDF version afterwards.
- Click File and then Save As.
- Click File Format towards the bottom of the window.
- Select the Output Format radio button Accessibility Conversion.
- Select PDF from the list of available file formats.
- Give your file a name, if needed, then click Export.
